Are all the UPSs the same?
The fundamental function of a UPS, that is to supply a clean and continuous power supply to a system, can be performed through different technical solutions.
These have peculiar characteristics that adapt more or less optimally according to the type of user to be protected.
On the market there are various UPS models, from the technically simple and inexpensive Stand-by to the Double Conversion, able to guarantee optimal protection even in the most critical applications.
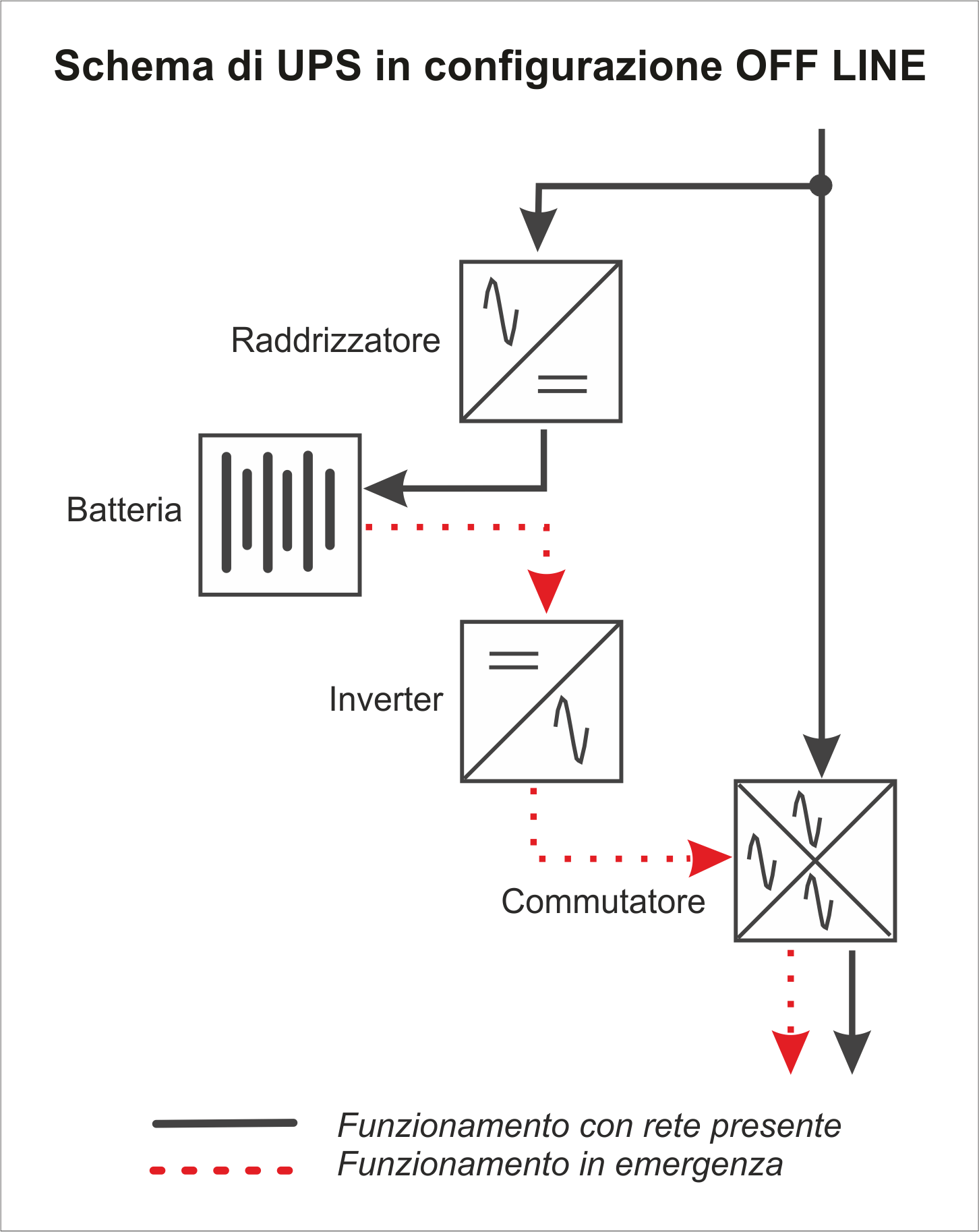
Stand-By / Off-Line / No-Break
Under normal conditions, the voltage of the primary supply line passes through the UPS where it is only "filtered" for a brief purge of radio disturbances.
In the event of a mains failure, the UPS draws the energy required for its operation from the battery and, through the inverter, feeds the load thus ensuring continuity of the supply.
The transfer time and the absence of an in-line voltage stabilizer can cause operational problems for modern systems and more sophisticated utilities and for areas with critical power supply; therefore it is not recommended to use it for the protection of professional systems and / or in areas with critical power supply.
The main advantage of this type of UPS is the relative simplicity of design that results in a lower cost of implementation.
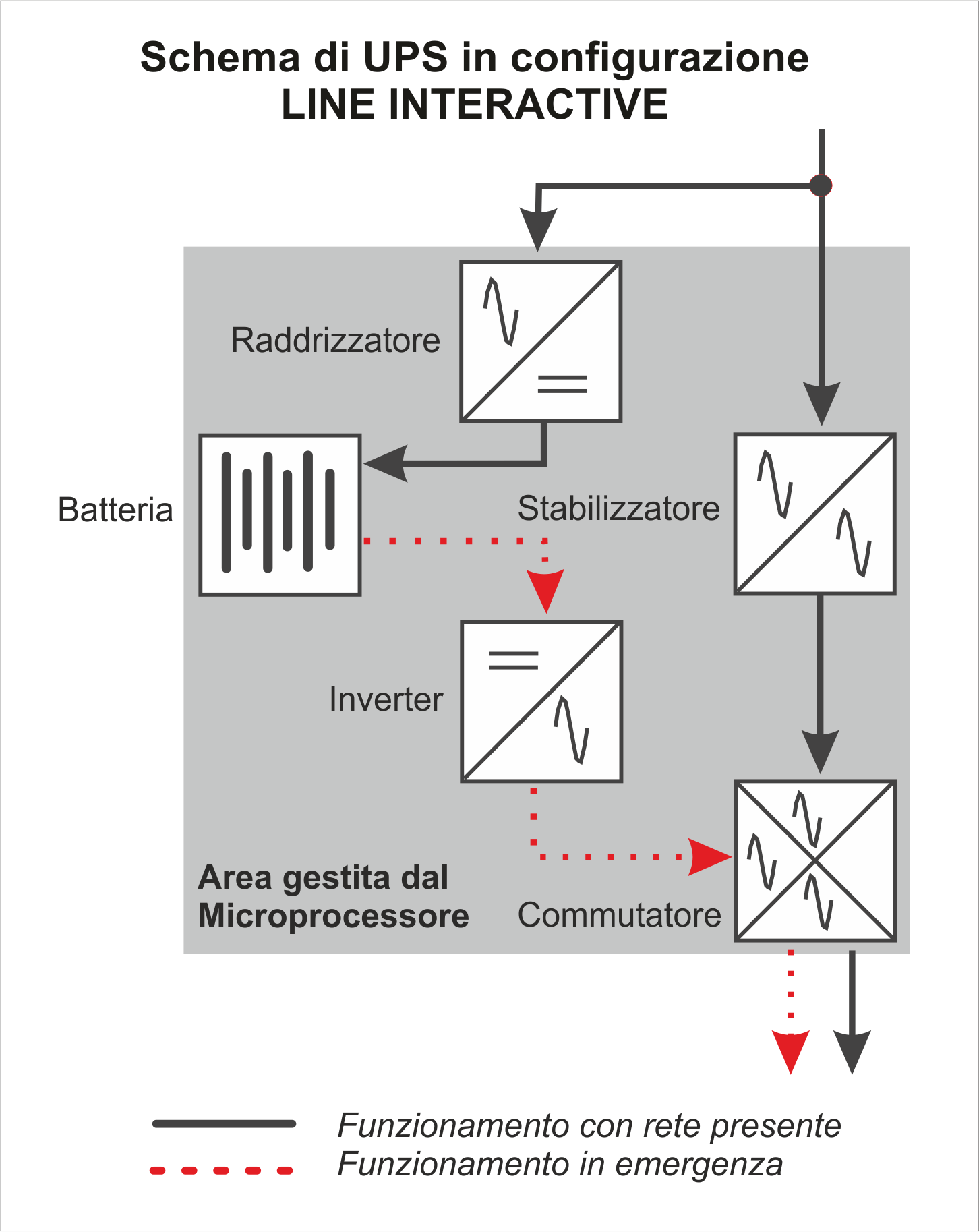
Line-Interactive
This configuration, characterized by an interactive operation with the network, guarantees high protection and constant conditioning of the primary supply line. Furthermore, a special internal microprocessor controls the quality of the energy supplied to the load, ensuring real-time corrections in case of need or anomalies.
The transfer time can be reduced up to 2 milliseconds, so as to allow full compatibility with all the most sophisticated operating systems in use today.
Line-Interactive UPS systems today represent an excellent technical solution, economically advantageous, to provide energy and protection control to IT and industrial systems even with high professional performance.
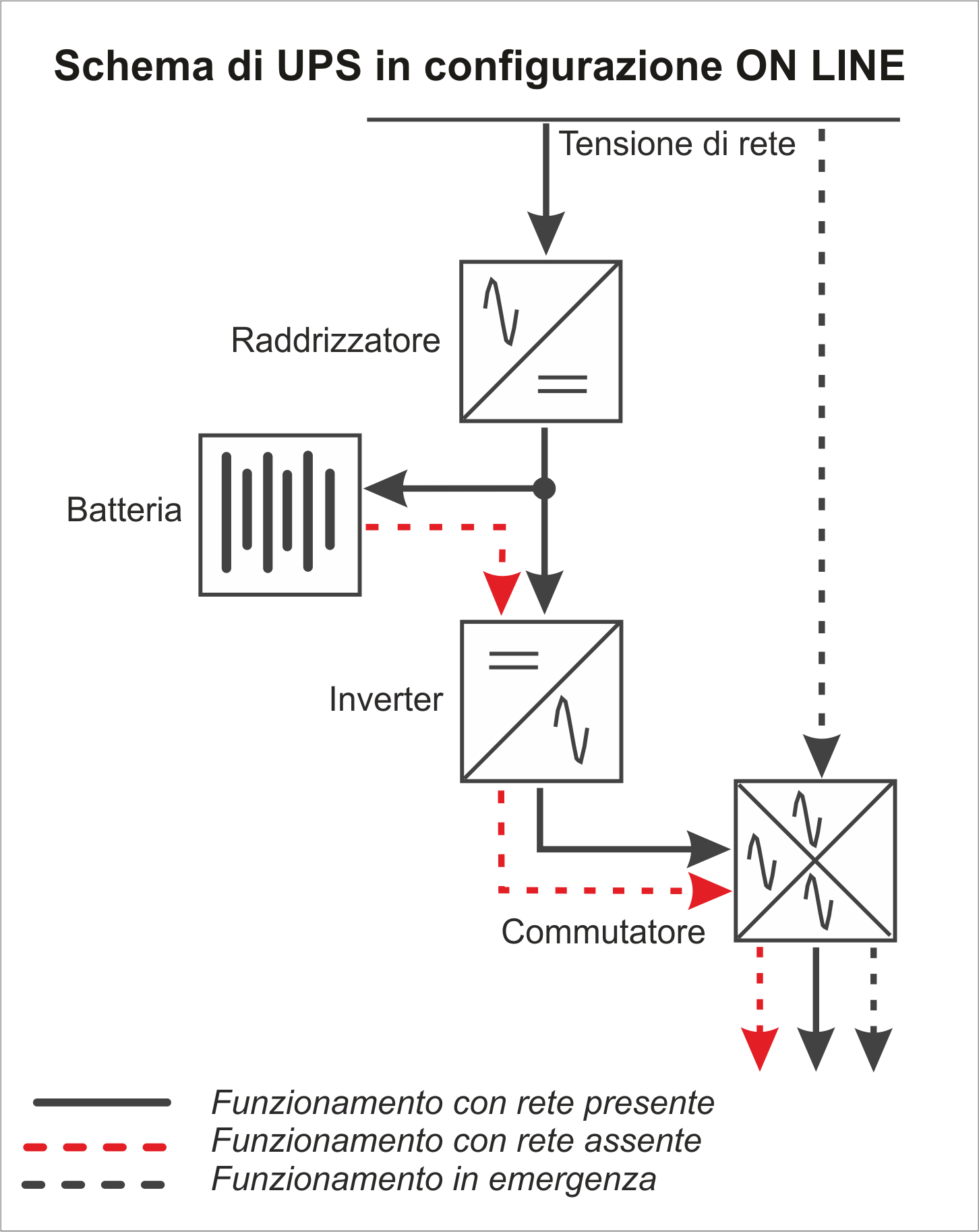
Double conversion On-Line
This is the only possible alternative when a data loss can have irreparable consequences (eg in medical or financial applications) or in particularly demanding situations such as in control applications in industrial processes or in areas with very critical power supply.
In this configuration, the input AC voltage / current is converted to DC by the Rectifier. Part of this charges the batteries while the rest is totally regenerated and goes to power the utilities in an ideal manner.
This technology is the only one that ensures the transfer to battery operation and vice versa without any solution of continuity.
In the event of an anomaly to the inverter and / or overload, some Double Conversion on-line UPSs are equipped with a reserve circuit (Operation in emergency) which guarantees power to the users thanks to the By-pass or Switch.This redundancy ensures maximum system protection.
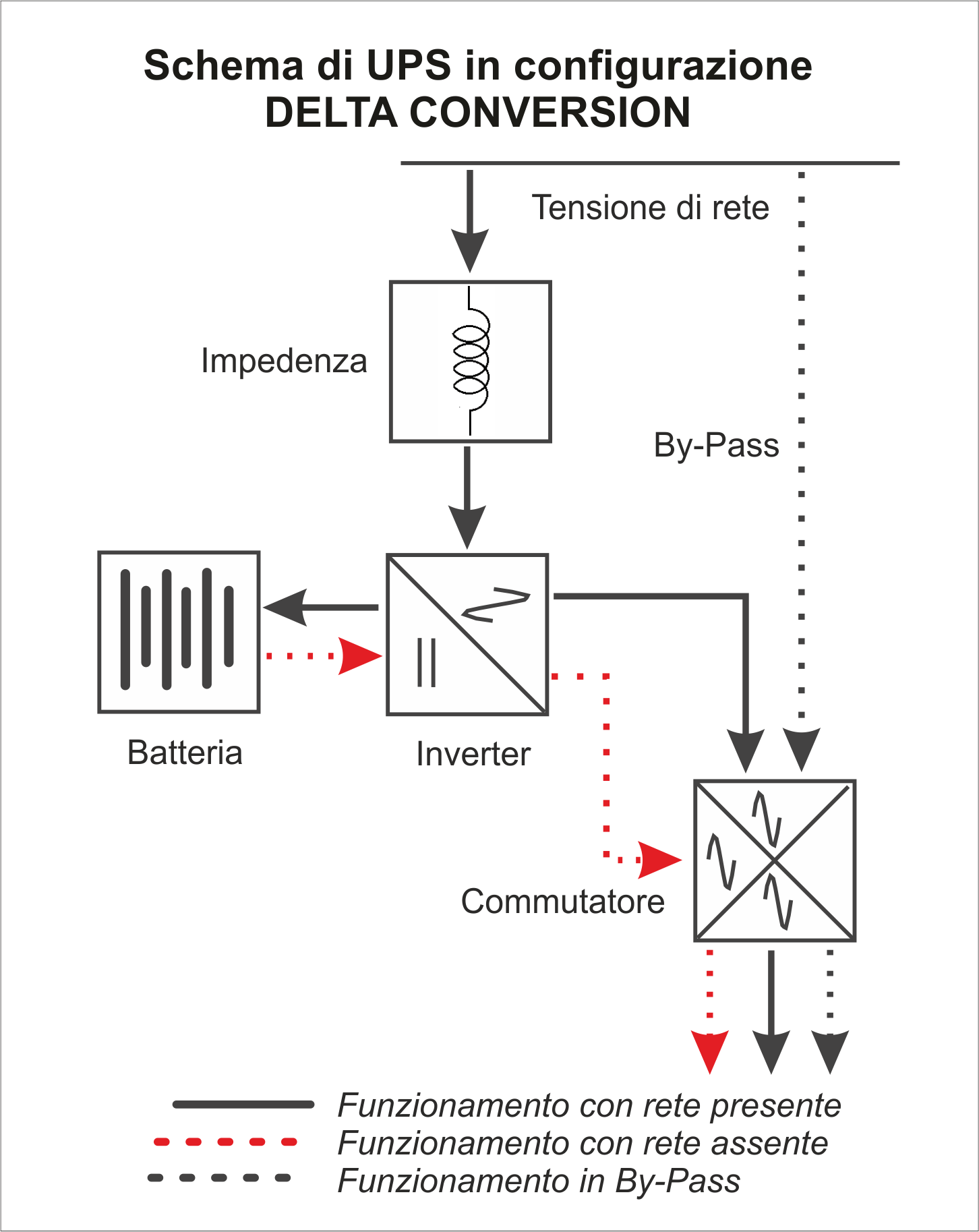
Delta-Conversion
Often confusedly confused with the Double Conversion Online UPSs, they actually have very distinct characteristics.
In this configuration, the inveter is always active and constantly stabilizes the voltage. The frequency, instead, depends totally on the incoming frequency.
They do not have any intervention time and perform a good voltage stabilization, like the Double Conversion Online UPS. But, unlike the latter, they do not carry out total isolation of users from the electricity grid.
In the event of an internal failure and / or overload, some Delta-Conversion UPSs are equipped with a backup circuit (By-pass) which guarantees power to the connected utilities.
The limit of these UPS is the too high price (due to the complex technology) for a protection slightly higher than that of the UPS Line-Interactive (much cheaper).